Search Docs by Keyword
Using SSH ControlMaster for Single Sign-On
OpenSSH has an option called ControlMaster that enables the sharing of multiple sessions over a single network connection. This means that you can connect to the cluster once, enter your password and verification code, and have all other subsequent ssh sessions (including svn, rsync, etc. that run over ssh) piggy-back off the initial connection without need for re-authentication. You can specify such options each time on the command line, but it’s easiest if you put it in your ssh client configuration file so that it applies every time.
Note that all port forwarding, including X display forwarding, must be setup by the initial connection and cannot be changed. For example, if you set up a master connection when sitting at your desktop, and then later ssh to the desktop itself and use that cannon connection, X programs that you run will open on the desktop’s display, not the display of the computer you’re now connecting to the desktop from. Likewise, if you forget to use -X on the initial connection, you will not be able to open X programs on subsequent connections.
Mac/Linux
On your Mac or linux desktop or laptop, create a text file ~/.ssh/config with, for example, the following contents:
Host cannon User myusername HostName login.rc.fas.harvard.edu ControlMaster auto ControlPath ~/.ssh/%r@%h:%p
where myusername is replaced appropriately.
This sets things up so that whenever you ssh to the host nickname cannon: ssh cannon
It will look for the special file (a socket) in your ~/.ssh/ directory that is maintaining a connection to the cluster. If it already exists and is open, it’ll use it to create a connection without re-authenticating; if it doesn’t exist, it’ll authenticate and create the file for subsequent use.
Note that all subsequent connections are dependent on the initial connection — if you exit or kill the initial connection all other ones die, too. This can obviously be annoying if it happens accidentally. It’s easily avoided by setting up a master connection in the background:
ssh -CX -o ServerAliveInterval=30 -fN cannon
The -fN make it go into the background and sit idle, after authenticating. (C for compression, X for X-forwarding, and -o ServerAliveInterval=30 to prevent dropped connections have nothing to do with the ControlMaster but are almost always helpful.)
Windows/PuTTY
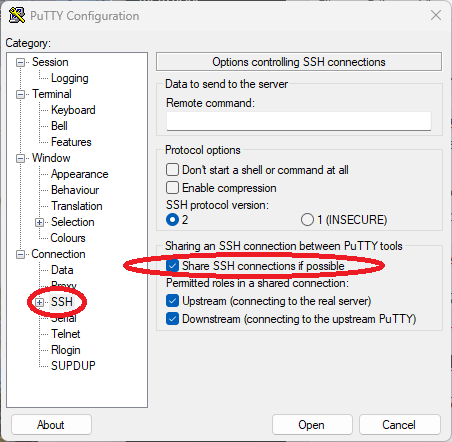
The PuTTY client for Windows also allows a ControlMaster setting under ‘Connection’ → ‘SSH’ → ‘Share SSH connections if possible’
One can also prevent dropped connections under ‘Connection’ → ‘Seconds between keepalives’
Bookmarkable Links
